ZTE ZXHN F670L is an AC1200 dual-band triple-play GPON gateway that provides four GE LAN ports and one phone port. It provides a dual-band concurrent Wi-Fi speed up to 1200 Mbps, allowing users to surf the internet, watch videos and play online games.
By doing certain custom setting, user can get a stable connectivity in LAN.
1. WLAN Settings
A. Local network WLAN Global Configuration 2.4 GHz
Certain custom settings of wireless LAN in 2.4 GHz band can help get better wireless network connectivity and stability. This include
- Setting Channel to Auto, allows the Wi-Fi router to automatically select a wireless channel in 2.4 GHz band that has low interference.
- In the Mode setting user can set the wireless standard that will used to host the wireless network in 2.4 GHz band. Setting the Mode to IEEE 802.11n Only disables the old wireless standards and uses only 802.11n network standard to host the wireless network.
- Selecting the "Australia" as the Country region in 2.4 GHz band opens up the channel number 12 and 13, that are free from interference. If there are restrictions on using certain channels in your country, then avoid changing Country region settings.
- Turning OFF the Short Guard interval(SGI) helps minimizing interference(ISI).
2.4 GHz WLAN Global Config_1
With the above points in consideration, this is the first config that can be done.
Do the following settings:
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN Global Configuration > 2.4 GHz setting.
- Channel : Auto
- Mode : IEEE 802.11n Only
- Country/Region: Australia
- Band Width: Auto
- SGI: Off
- Click Apply button.
2.4 GHz WLAN Global Config_2
Restrict the bandwidth to 20 MHz, when there are multiple wireless network in the area and 2.4 GHz channels are congested.
- Setting the Bandwidth to 20 MHz gives better stability and avoid interference.
Do the following settings:
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN Global Configuration > 2.4 GHz setting.
- Channel : Auto
- Mode : IEEE 802.11n Only
- Country/Region: Australia
- Band Width: 20MHz
- SGI: Off
- Click Apply button.
2.4 GHz WLAN Global Config_3
Manually setting the 2.4 GHz channel helps in minimizing interference if the user know the channel that is least congested.
Do the following settings:
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN Global Configuration > 2.4 GHz setting.
- Channel : 13
- Mode : IEEE 802.11n Only
- Country/Region: Australia
- Band Width: 20 MHz
- SGI: Off
- Click Apply button.
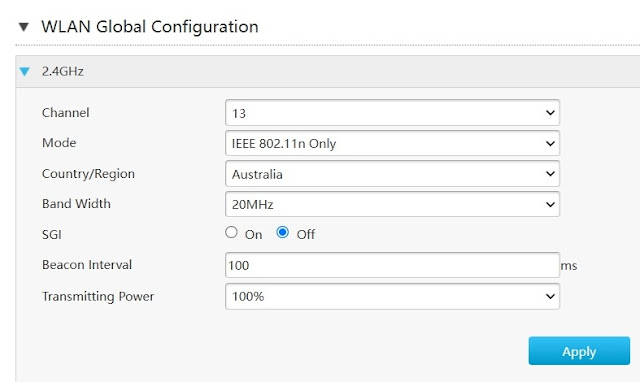
2.4 GHz WLAN Global Config_4
The Beacon Interval in a WiFi network, which determines how frequently the access point (AP) broadcasts beacon frames, significantly impacts client devices in several key areas:
1. Network Discovery & Connection Time
- Shorter Interval (e.g., 50 ms):
- Pros: Faster network discovery for clients, reducing time to connect or roam between APs. Beneficial for mobile devices in dynamic environments.
- Cons: Increased channel occupancy, potentially causing higher contention and reduced throughput in dense networks.
Longer Interval (e.g., 200 ms):
- Pros: Reduces management frame overhead, freeing airtime for data transmission.
- Cons: Slower network detection, leading to delayed initial connections or roaming decisions.
2. Power Consumption (Battery Life)
- Shorter Interval: Devices in power-saving mode wake up more frequently to check for buffered data (via DTIM beacons), draining battery faster.
- Longer Interval: Extends sleep periods for clients, improving battery life (ideal for IoT devices), but may introduce latency in data delivery.
3. Roaming Performance
- Shorter Interval: Enables quicker signal strength assessment, promoting smoother handoffs between APs and reducing dropped connections.
- Longer Interval: May delay roaming decisions, risking temporary signal loss or degraded performance during movement.
4. Network Overhead vs. Throughput
- Shorter Interval: Higher overhead from frequent beacons reduces available bandwidth for data, impacting throughput in congested environments.
- Longer Interval: Minimizes overhead, optimizing airtime for data transfer, beneficial in high-traffic networks.
- User may increase the Beacon interval, if client devices support it.
- Preferred beacon interval values: 150, 200, 250
- After setting the Beacon interval other than default value, user need to monitor the client devices for connectivity and stability issues.
If you want to manually set the Beacon Interval then do the following settings:
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN Global Configuration > 2.4 GHz setting.
- Beacon Interval: 200 ms
- Click Apply button.
B. Local Network WLAN Global Configuration 5 GHz
In this setting, user can do the custom settings for the wireless network in 5 GHz band.
- Setting Channel to Auto, allows the Wi-Fi router to automatically select a wireless channel in 2.4 GHz band that has low interference.
- In the Mode setting user can set the wireless standard that will used to host the wireless network in 5 GHz band. Setting the Mode to IEEE 802.11ac Only disables the old wireless standards and uses only 802.11ac network standard to host the wireless network.
- Selecting the "Australia" as the Country region in 5 GHz band, opens up the channel number 52, 56, 60 ,64 (UNII-2) and 100, 104, 108,112 (UNII-E).
- Turning OFF the Short Guard interval(SGI) helps minimizing interference(ISI).
5 GHz WLAN Global Config_1
With the above points in consideration this is the first config that can be done.
Do the following settings
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN Global Configuration > 5 GHz setting.
- Channel: Auto
- Mode: IEEE 802.11ac Only
- Country/Region: Australia
- Band Width: Auto
- SGI: Off
- Beacon Interval: 100ms
- Transmitting Power : 100%
- Click Apply button.
5 GHz WLAN Global Config_2
Manually setting the 5 GHz channel helps in minimizing interference if the user know the channel number that is least congested.
If you want to manually set the 5 GHz channel then do the following settings:
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN Global Configuration > 5 GHz setting.
- Channel: 36
- Mode: IEEE 802.11ac Only
- Country/Region: Australia
- Band Width: Auto
- SGI: Off
- Beacon Interval: 100 ms
- Transmitting Power: 100%
- Click Apply button.
5 GHz WLAN Global Config_3
The Beacon Interval in a WiFi network, which determines how frequently the access point (AP) broadcasts beacon frames, significantly impacts client devices in several key areas:
The Beacon Interval in a WiFi network, which determines how frequently the access point (AP) broadcasts beacon frames, significantly impacts client devices in several key areas:
1. Network Discovery & Connection Time
- Shorter Interval (e.g., 50 ms):
- Pros: Faster network discovery for clients, reducing time to connect or roam between APs. Beneficial for mobile devices in dynamic environments.
- Cons: Increased channel occupancy, potentially causing higher contention and reduced throughput in dense networks.
Longer Interval (e.g., 200 ms):
- Pros: Reduces management frame overhead, freeing airtime for data transmission.
- Cons: Slower network detection, leading to delayed initial connections or roaming decisions.
2. Power Consumption (Battery Life)
- Shorter Interval: Devices in power-saving mode wake up more frequently to check for buffered data (via DTIM beacons), draining battery faster.
- Longer Interval: Extends sleep periods for clients, improving battery life (ideal for IoT devices), but may introduce latency in data delivery.
3. Roaming Performance
- Shorter Interval: Enables quicker signal strength assessment, promoting smoother handoffs between APs and reducing dropped connections.
- Longer Interval: May delay roaming decisions, risking temporary signal loss or degraded performance during movement.
4. Network Overhead vs. Throughput
- Shorter Interval: Higher overhead from frequent beacons reduces available bandwidth for data, impacting throughput in congested environments.
- Longer Interval: Minimizes overhead, optimizing airtime for data transfer, beneficial in high-traffic networks.
- User may increase the Beacon interval, if client devices support it.
- Preferred beacon interval values: 150, 200, 250
- After setting the Beacon interval other than default value, user need to monitor the client devices for connectivity and stability issues.
If you want to manually set the Beacon Interval then do the following settings:
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN Global Configuration > 5 GHz setting.
- Beacon Interval: 200 ms
- Click Apply button.
2. LAN IPv4 DHCP Settings
It is recommended to change the default setting of the IPv4 DHCP server to achieve better stability of the LAN network.
Do the following custom DHCP server setting:
- Open Local Network > LAN > IPv4 > DHCP Server setting.
- DHCP Server : On
- LAN IP Address: 192.168.100.1
- Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
- DHCP Start IP Address: 192.168.100.2
- DHCP End IP Address: 192.168.100.254
- Click Apply button.
Note: After this setting the IP address of the ZTE router will be 192.168.100.1
3. IPv4 DNS setting for Block ads
A. IPv4 DNS Config_1
User can do custom DNS server setting to block ads.
To set custom DNS server setting do the followings:
- Open Local Network > LAN > IPv4 > DHCP Server setting.
- ISP DNS: Off
- Primary DNS : 94.140.14.15
- Secondary DNS: 94.140.15.16
- Click Apply button.
B. IPv4 DNS Config_2
User may use multiple DNS service providers in case one is not able to resolve the required IP Address.
- AdGuard DNS: 94.140.14.15
- Cloudflare DNS: 1.1.1.3
To set custom DNS server setting do the followings:
- Open Local Network > LAN > IPv4 > DHCP Server setting.
- ISP DNS: Off
- Primary DNS : 94.140.14.15
- Secondary DNS: 1.1.1.3
- Click Apply button.
4. Local Network DNS Settings
Local network DNS setting can be used to set the custom DNS server that will be assigned to the devices connecting to the LAN.
Blocking ads at DNS level lowers the load on internet traffic. Thus it speeds up overall internet experience.
A. DNS Server Setting 1
Example : Adguard DNS server can be use to block the ads on devices connected to the LAN.
To configure the Local network DNS setting, do the following:
- Open Local Network > DNS setting.
- IPv4 DNS Server1: 94. 40.14.15
- IPv4 DNS Server2: 94. 40.15.16
- IPv6 DNS Server1: 2a10:50c0::bad1:ff
- IPv6 DNS Server2: 2a10:50c0::bad2:ff
- Click Apply button.
B. DNS Server Setting 2
Using multiple DNS service provider makes sure that IP address of websites get resolved using any one of the DNS servers.
Example :
- IPv4 Adguard DNS server: 94. 40.14.15
- IPv4 Cloudflare DNS: 1.1.1.3
- IPv6 Adguard DNS server: 2a10:50c0::bad1:ff
- IPv6 Cloudflare DNS: 2606:4700:4700::1113
To configure the Local network DNS setting, do the following:
- Open Local Network > DNS setting.
- IPv4 DNS Server1: 94. 40.14.15
- IPv4 DNS Server2: 1.1.1.3
- IPv6 DNS Server1: 2a10:50c0::bad1:ff
- IPv6 DNS Server2: 2606:4700:4700::1113
- Click Apply button.
C. DHCPv6 Server setting
User need to configure the LAN IPv6 DHCPv6 Server setting as shown :
- DHCPv6 Server: On
- DNS Delegate Type: Auto , DNS Address Specified
- Click Apply button.
D. IPv6 RA Service setting
In IPv6 Router Advertisements (RAs), the router can include an MTU option. This option informs hosts on the link about the recommended MTU they should use for packets destined for off-link destinations.
By advertising an MTU, the router suggests a starting point for hosts performing PMTU to destinations beyond the local link. This can prevent some initial packet fragmentation and the resulting ICMPv6 "Packet Too Big" messages, leading to more efficient communication.
- Enabe Specify MTU.
- Set MTU value to 1300.
5. WLAN Encryption Type
Use WPA2 AES encryption method enhances security and is faster compared to older WPA encryption method.
That's why user must use WPA2 encryption method for wireless network security.
- Open Local Network > WLAN > WLAN Basic > WLAN SSID Configuration setting.
- Select the option WPA2-PSK-AES as Encryption Type for each SSID.
- Click Apply button.
6. WLAN SSID Configuration
When creating wireless network in 2.4 GHz, give preference to the SSID1 (2.4GHz) config..
When creating wireless network in 5 GHz, give preference to the SSID5 (5 GHz) config.
7. SNTP Server Setting
Configuring a proper NTP server setting will set the correct date and time in the router.
To do so do the following:
- Open Internet > SNTP setting.
- Set Primary NTP Server as 0.in.pool.ntp.org
- Set Secondary NTP Server as 1.in.pool.ntp.org
- Click Apply button.















